5. expression parsing functions
Now we we will need to implement functions to parse all of the other expressions that we need. And we need to add those expressions to our expression enum, and also update token stats.
Implementation
Section titled “Implementation”Assignment
Section titled “Assignment”Will be called when parsing = += -= *= /= tokens.
It will be used when eg.
a += 52It needs to know value, operator and target to assign.
pub fn assignment(parser: &mut Parser, left: Expression, _: i8) -> Result<Expression> { let operator = parser.advance().to_owned(); let value = Box::new(expression(parser, 0)?); Ok(Expression::Assignment { target: Box::new(left), operator, value, debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}Increment && Decrement
Section titled “Increment && Decrement”It’s basically an assignment but without a value
⚠️ Implementation
pub fn decrement(parser: &mut Parser, left: Expression, _: i8) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::MinusMinus)?; Ok(Expression::Decrement { target: Box::new(left), debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}pub fn increment(parser: &mut Parser, left: Expression, _: i8) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::PlusPlus)?; Ok(Expression::Increment { target: Box::new(left), debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}Type conversion
Section titled “Type conversion”We have already implemented a nod function for a ’(’ token - grouping expression, eg. 2 * (52 - 22)
But in c to convert type of a variable you do: bool z = (bool)1
So to differentiate this we will check if inside of the parentheses there is an identifier, and if it’s value is inside the parser::valid_data_type_names.
The type conversion itself has to know it’s type and value it converts - next expression
⚠️ Implementation
pub fn open_paren(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::OpenParen)?;
let current = parser.current(); if current.kind == TokenKind::Identifier && parser .valid_data_type_names .contains(current.value.as_str()) { let data_type = types::parse(parser).context("open_paren -> TypeConversion -> data_type")?; parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseParen)?; let value = expression(parser, 0).context("open_paren -> TypeConversion -> value")?;
Ok(Expression::TypeConversion { value: Box::new(value), data_type, debug_data: parser.debug_data(), }) } else { let value = Box::new(expression(parser, 0)?);
parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseParen)?; Ok(Expression::Grouping { value, debug_data: parser.debug_data(), }) }}Dereference
Section titled “Dereference”void do_smth(int *to_modify){...*to_modify = 5;...}You dereference a pointer by putting a star before a name of a variable. dereferencing is a fancy way of saying ‘access a value inside a pointer’.
⚠️ Implementation
pub fn dereference(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::Star)?; let value = expression(parser, 0)?;
Ok(Expression::Dereference { value: Box::new(value), debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}Access reference
Section titled “Access reference”int a = 25;int *ptr = &a;basically a reversed dereference
⚠️ Implementation
pub fn access_reference(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::Reference)?; let value = expression(parser, 0)?;
Ok(Expression::AccessReference { value: Box::new(value), debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}Static
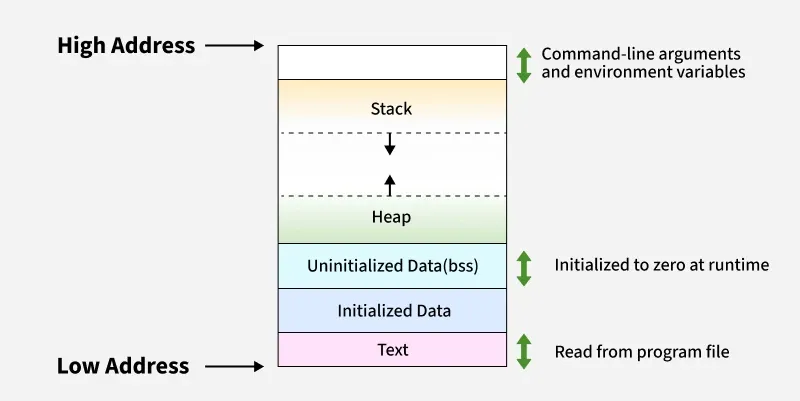
Section titled “Static” static int count = 0;In C, static keyword tells the compiler to store this variable on .data/.bss instead of the stack.
⚠️ Implementation
pub fn static_expr(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::Static)?; let value = expression(parser, 0)?; Ok(Expression::Static { value: Box::new(value), debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}Member
Section titled “Member” some.thing.to.access = 2;Required data:
- the thing it accesses - left
- value - right
⚠️ Implementation
pub fn member_expr(parser: &mut Parser, left: Expression, _: i8) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::Dot)?; let right = expression(parser, 0).with_context(|| format!("member expr-> left:{:?}", left))?;
Ok(Expression::MemberExpr { left: Box::new(left), right: Box::new(right), debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}Boolean
Section titled “Boolean”Just convert true/false tokens into boolean
⚠️ Implementation
pub fn boolean(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { let token = parser.advance(); return Ok(Expression::Boolean( match token.kind { crate::lexer::token::TokenKind::True => true, crate::lexer::token::TokenKind::False => false, _ => { bail!( "expected to find token of kind either True or False, found: '{:?}'", token.kind ) } }, parser.debug_data(), ));}String
Section titled “String”Just take value from the token
⚠️ Implementation
pub fn string(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { let token = parser.advance();
return Ok(Expression::String( token.value.to_owned(), parser.debug_data(), ));}CompilerData
Section titled “CompilerData”#include "this part also should be included"This is all you should need to implement this.
⚠️ Implementation
pub fn compiler_data(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { Ok(Expression::CompilerData( parser.advance().value.to_owned(), parser.debug_data(), ))}Open curly
Section titled “Open curly”In C there are many things that could be wrapped in curly braces, thank fully most of them will be parsed by functions called when encountering a keyword beforehand eg. if (...) {if statement contents} or int test(){function contents}.
This allows us to only have to think about 2 cases.
- creating a new ‘scope’
int test_fn(){ { int var_name = 25; } int var_name = 55;}- initializing a struct
myStructure s1 = {13, 'B', "Some text"};We will need to first check with which case we are dealing and than call appropriate function.
Scope block
Section titled “Scope block”Scope block will just consist of an array of expressions that represent lines inside of it.
We will be just parsing expressions until we encounter a right curly brace.
Struct initialization
Section titled “Struct initialization”To initialize a struct we just need to know values inside the initialization that we will be assigning.
This may seem hard at first, but actually is pretty easy, coma has a low binding power so parsing expressions, with binding power of 0, in a loop and moving past comas will give us needed values.
⚠️ Implementation
pub fn parse_open_curly(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::OpenCurly)?; // this might not be the best way to do this, but i don't see another one for now if parser.next().kind == TokenKind::Comma { parse_data_structure_initialization(parser) } else { new_code_block(parser) }}
pub fn new_code_block(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { let mut inside = Vec::new(); while parser.current().kind != TokenKind::CloseCurly { inside.push(parsing_functions::expression(parser, 0).with_context(|| { format!( "debug data: {:?},\n parsed expressions:{:#?}", parser.debug_data(), inside ) })?); if parser.current().kind == TokenKind::SemiColon { parser.advance(); } } parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseCurly)?;
Ok(Expression::NewCodeBlock { inside, debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}pub fn parse_data_structure_initialization(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { let mut values = Vec::new(); loop { let value = expression(parser, 0)?; values.push(value); if parser.current().kind == TokenKind::CloseCurly { break; } parser.expect(TokenKind::Comma)?; } parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseCurly)?;
Ok(Expression::DataStructureInitialization { values, debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}Identifier Token
Section titled “Identifier Token”In rust for example you write let when you declare a variable or fn when you declare a function.
In c compiler must ‘guess’ your intention.
To accomplish this we will use the parser::valid_data_type_names.
If the value of a token isn’t inside of the parser::valid_data_type_names we will just output an identifier expression with it’s value.
We need to use types::parse() to get data type that we will be using for next expressions.
Than we need to check if the next token is a identifier:
a. it is: we take it’s value as a name for variable/function.
b. it isn’t: just return a ‘DataTypeAccess’ expression with the data type that we parsed before.
Than we need to check for array declaration, because in c you put square brackets after a variable name: int array[][] = ...; .
So we use types::wrap_data_type_in_an_array for this.
Next we need to check weather we are dealing with a function or variable declaration. We can do it by checking if the next token is a ’(’.
For variable declaration we know everything that we need so we will just return expression with variable name and type.
Now we need to deal with function declaration:
int* func(int param,char* text){...}---------//this is the part that we have already parsedParsing function parameters
Section titled “Parsing function parameters”we will do the same as during parsing the struct declaration, but than we need to read value of the next character as a name.
Parsing function contents
Section titled “Parsing function contents”this is the same as when parsing a scope block.
Than we need to just return a function expression with: name, data type, parameters, and contents.
⚠️ Implementation
use crate::{ lexer::token::TokenKind, parse, parser::{ Parser, expression::{Expression, Property}, parsing_functions::{self}, types::{self, DataType}, },};
use anyhow::{Context, Result};pub fn identifier(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { let first = parser.current().to_owned();
if parser.valid_data_type_names.contains(&first.value) { handle_function_or_variable_declaration(parser) .with_context(|| format!("identifier - data type name: {}", first.value.as_str())) } else { parser.expect(first.kind)?; Ok(Expression::Identifier(first.value, parser.debug_data())) }}
pub fn handle_function_or_variable_declaration(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { let mut data_type = types::parse(parser) .context("parse data type for: handle_function_or_variable_declaration")?; if parser.current().kind != TokenKind::Identifier { return Ok(Expression::DataTypeAccess { data_type: data_type, debug_data: parser.debug_data(), }); }
let name = parser.advance().to_owned();
data_type = types::wrap_data_type_in_an_array(data_type, parser)?;
if parser.current().kind == TokenKind::OpenParen { handle_function_declaration(data_type, name.value, parser) .context("handle_function_declaration") } else { Ok(Expression::VariableDeclaration { var_type: data_type, name: name.value, debug_data: parser.debug_data(), }) }}fn handle_function_declaration( output_data_type: DataType, name: String, parser: &mut Parser,) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::OpenParen)?;
let mut properties = Vec::new();
if parser.current().kind != TokenKind::CloseParen { loop { let data_type = types::parse(parser).context("parse function input data types")?; let name = parser.expect(TokenKind::Identifier)?.value.to_owned(); properties.push(Property { var_name: name, var_type: data_type, }); if parser.current().kind == TokenKind::CloseParen { break; } parser .expect(TokenKind::Comma) .context("function properties")?; } } parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseParen)?; parser.expect(TokenKind::OpenCurly)?;
let mut inside = Vec::new(); while parser.current().kind != TokenKind::CloseCurly { inside.push(parsing_functions::expression(parser, 0).context("inside function")?); if parser.current().kind == TokenKind::SemiColon { parser.advance(); } }
parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseCurly)?; Ok(Expression::Function { name, properties, output: output_data_type, inside: inside, debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}If / else
Section titled “If / else”if(condition && !other_thing){contents}else if(a>0){contents}else{contents}It is possible to chain multiple else if-s and every one has it’s contents and conditions.
Also we need to remember to expect all of the parentheses and curly brackets and keywords like if and else.
To parse conditions we will just use parsing_functions::expression with binding power of 0.
It should nicely parse all of the conditions at once and leave parentheses thanks to the binding power of all of the tokens.
⚠️ Implementation
pub fn parse_if(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::If)?; parser.expect(TokenKind::OpenParen)?; let condition = parsing_functions::expression(parser, 0)?; parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseParen)?; parser.expect(TokenKind::OpenCurly)?; let mut inside = Vec::new(); while parser.current().kind != TokenKind::CloseCurly { inside.push(parsing_functions::expression(parser, 0)?); parser .expect(TokenKind::SemiColon) .context("expected to find a semicolon after a expression - function contents")?; } parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseCurly)?;
let mut chained_elses = Vec::new();
while parser.current().kind == TokenKind::Else { let (else_value, break_else) = parse_else(parser)?; chained_elses.push(else_value); if break_else { break; } }
Ok(Expression::If { condition: Box::new(condition), inside, chained_elses, debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}fn parse_else(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<(Expression, bool)> { parser.expect(TokenKind::Else)?; let (break_else, condition) = if parser.current().kind == TokenKind::If { parser.expect(TokenKind::If)?; parser.expect(TokenKind::OpenParen)?; let condition = parsing_functions::expression(parser, 0)?; parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseParen)?; (false, Some(Box::new(condition))) } else { (true, None) }; parser.expect(TokenKind::OpenCurly)?;
let mut inside = Vec::new(); while parser.current().kind != TokenKind::CloseCurly { inside.push(parsing_functions::expression(parser, 0)?); parser .expect(TokenKind::SemiColon) .context("expected to find a semicolon after a expression - function contents")?; } parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseCurly)?; Ok(( Expression::Else { condition, inside, debug_data: parser.debug_data(), }, break_else, ))}while (i >25){ i/2;}Parsing while loop isn’t different from parsing if-s in almost any way. You need to read condition and contents.
⚠️ Implementation
pub fn parse_while(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::While)?; parser.expect(TokenKind::OpenParen)?; let condition = parsing_functions::expression(parser, 0)?; parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseParen)?; parser.expect(TokenKind::OpenCurly)?; let mut inside = Vec::new(); while parser.current().kind != TokenKind::CloseCurly { inside.push(parsing_functions::expression(parser, 0)?); parser .expect(TokenKind::SemiColon) .context("expected to find a semicolon after a expression - function contents")?; } parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseCurly)?;
Ok(Expression::While { condition: Box::new(condition), inside, debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}Just return expression with debug data inside and expect token of kind Break.
⚠️ Implementation
pub fn break_expr(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::Break)?; return Ok(Expression::Break { debug_data: parser.debug_data(), });}for(int i =0;i<25;i++){...}To parse for loop we basically need to use parsing_functions::expression 3 times and than parse contents
⚠️ Implementation
pub fn parse_for(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { // for(int i =0;i<25;i++){ // ... // } parser.expect(TokenKind::For)?; parser.expect(TokenKind::OpenParen)?; let iterator_init = Box::new(parsing_functions::expression(parser, 0)?); parser.expect(TokenKind::SemiColon)?; let condition = Box::new(parsing_functions::expression(parser, 0)?); parser.expect(TokenKind::SemiColon)?; let incr = Box::new(parsing_functions::expression(parser, 0)?); parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseParen)?;
parser.expect(TokenKind::OpenCurly)?; let mut inside = Vec::new(); while parser.current().kind != TokenKind::CloseCurly { inside.push(parsing_functions::expression(parser, 0)?); parser .expect(TokenKind::SemiColon) .context("expected to find a semicolon after a expression - function contents")?; } parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseCurly)?;
Ok(Expression::For { iterator_init, condition, incr, inside, debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}Typedef
Section titled “Typedef”typedef struct { char brand[2]; int year;} Car;Type def tells our compiler that we want to create a new data type with some name - push it into Parser::valid_data_type_names
To parse it we need to parse data type and name.
⚠️ Implementation
pub fn type_def(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::Typedef)?; let data_type = types::parse(parser).context("type_def -> data_type")?; let name = parser .expect(TokenKind::Identifier) .context("type_def -> name")? .value;
parser.valid_data_type_names.insert(name.to_string());
Ok(Expression::Typedef { data_type, name, debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}array access
Section titled “array access”smth = array[x+2];We need to know expression that we are accessing, and index.
⚠️ Implementation
pub fn array_access(parser: &mut Parser, left: Expression, _: i8) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::OpenBracket)?; let index = expression(parser, 0)?;
parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseBracket)?; Ok(Expression::ArrayAccess { left: Box::new(left), index: Box::new(index), debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}Function call
Section titled “Function call”func_name(i,x/25,car.name.char());this will be called by open parentheses.
Needed data:
- expression on the left
- function parameters
⚠️ Implementation
pub fn function_call(parser: &mut Parser, left: Expression, _: i8) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::OpenParen)?; let mut properties = Vec::new(); loop { let current_token = parser.current().to_owned(); properties.push( expression(parser, 0).with_context(|| { format!("function call- parse input values-> {:?}", current_token) })?, );
if parser.current().kind == TokenKind::CloseParen { break; } parser.advance(); } parser .expect(TokenKind::CloseParen) .context("function_cal -> end paren")?;
Ok(Expression::FunctionCall { left: Box::new(left), values: properties, debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}Return
Section titled “Return”return a+b;⚠️ Implementation
pub fn return_expr(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::Return)?; let value = expression(parser, 0)?; Ok(Expression::Return { value: Box::new(value), debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}as you can see implementing a c parser is a pretty easy task but it requires a lot of repetitive work.
Adding token stats
Section titled “Adding token stats”Now we need to assign our newly implemented functions to be called by right tokens.
Look at all tokens in token stats functions inside parser/token_stats.rs and think which functions seem appropriate to use.
If you are not sure go back to the part where we were implementing certain function and think where it should be used.
At the end:
Section titled “At the end:”⚠️ Implementation
use crate::{ lexer::token::{Token, TokenKind}, parser::types::DataType,};
#[derive(Debug, Clone)]pub struct DebugData { pub line: u16, pub file: String,}
#[derive(Debug, Clone)]pub struct Property { pub var_name: String, pub var_type: DataType,}
#[derive(Debug, Clone)]pub enum Expression { Skip, Increment { target: Box<Expression>, debug_data: DebugData, }, Decrement { target: Box<Expression>, debug_data: DebugData, }, DataStructureInitialization { values: Vec<Expression>, debug_data: DebugData, }, TypeConversion { value: Box<Expression>, data_type: DataType, debug_data: DebugData, }, Typedef { data_type: DataType, name: String, debug_data: DebugData, }, Dereference { value: Box<Expression>, debug_data: DebugData, }, Boolean(bool, DebugData),
Number(u32, DebugData),
CompilerData(String, DebugData), String(String, DebugData), Identifier(String, DebugData), Prefix { prefix: Token, value: Box<Expression>, debug_data: DebugData, }, // target operator value Assignment { target: Box<Expression>, operator: Token, value: Box<Expression>, debug_data: DebugData, }, // type name mutable DataTypeAccess { data_type: DataType, debug_data: DebugData, }, VariableDeclaration { var_type: DataType, name: String, debug_data: DebugData, }, Grouping { value: Box<Expression>, debug_data: DebugData, }, Struct { public: bool, name: String, properties: Vec<Property>, functions: Vec<Expression>,
debug_data: DebugData, }, NewCodeBlock { inside: Vec<Expression>, debug_data: DebugData, },
Binary { left: Box<Expression>, operator: Token, right: Box<Expression>, debug_data: DebugData, }, Function { name: String, properties: Vec<Property>, output: DataType, inside: Vec<Expression>, debug_data: DebugData, },
MemberExpr { left: Box<Expression>, right: Box<Expression>,
debug_data: DebugData, }, AccessReference { value: Box<Expression>,
debug_data: DebugData, }, Break { debug_data: DebugData, }, Return { value: Box<Expression>,
debug_data: DebugData, }, If { condition: Box<Expression>, inside: Vec<Expression>,
/// those will be else statements with or without conditions chained_elses: Vec<Expression>, debug_data: DebugData, }, Else { condition: Option<Box<Expression>>, inside: Vec<Expression>,
debug_data: DebugData, }, ArrayAccess { left: Box<Expression>, index: Box<Expression>,
debug_data: DebugData, },
While { condition: Box<Expression>, inside: Vec<Expression>,
debug_data: DebugData, }, Static { value: Box<Expression>, debug_data: DebugData, },
For { iterator_init: Box<Expression>, condition: Box<Expression>, incr: Box<Expression>, inside: Vec<Expression>,
debug_data: DebugData, }, FunctionCall { left: Box<Expression>, values: Vec<Expression>, debug_data: DebugData, },} ```
``` rust//parser/parsing_functions/data_parsing.rsuse crate::parser::{Parser, expression::Expression};use anyhow::{Result, bail};
pub fn string(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { let token = parser.advance();
return Ok(Expression::String( token.value.to_owned(), parser.debug_data(), ));}
pub fn number(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { let token = parser.advance();
return Ok(Expression::Number( str_to_num(&token.value)?, parser.debug_data(), ));}pub fn str_to_num(s: &str) -> Result<u32, std::num::ParseIntError> { if let Some(hex) = s.strip_prefix("0x") { u32::from_str_radix(hex, 16) } else if let Some(bin) = s.strip_prefix("0b") { u32::from_str_radix(bin, 2) } else if let Some(oct) = s.strip_prefix("0o") { u32::from_str_radix(oct, 8) } else { // default to decimal s.parse::<u32>() }}
pub fn boolean(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { let token = parser.advance(); return Ok(Expression::Boolean( match token.kind { crate::lexer::token::TokenKind::True => true, crate::lexer::token::TokenKind::False => false, _ => { bail!( "expected to find token of kind either True or False, found: '{:?}'", token.kind ) } }, parser.debug_data(), ));}use crate::{ lexer::token::TokenKind, parser::{ Parser, expression::{Expression, Property}, parsing_functions::{self}, types::{self, DataType}, },};
use anyhow::{Context, Result};pub fn identifier(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { let first = parser.current().to_owned();
if parser.valid_data_type_names.contains(&first.value) { handle_function_or_variable_declaration(parser) .with_context(|| format!("identifier - data type name: {}", first.value.as_str())) } else { parser.expect(first.kind)?; Ok(Expression::Identifier(first.value, parser.debug_data())) }}
pub fn handle_function_or_variable_declaration(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { let mut data_type = types::parse(parser) .context("parse data type for: handle_function_or_variable_declaration")?; if parser.current().kind != TokenKind::Identifier { return Ok(Expression::DataTypeAccess { data_type: data_type, debug_data: parser.debug_data(), }); }
let name = parser.advance().to_owned();
data_type = types::wrap_data_type_in_an_array(data_type, parser)?;
if parser.current().kind == TokenKind::OpenParen { handle_function_declaration(data_type, name.value, parser) .context("handle_function_declaration") } else { Ok(Expression::VariableDeclaration { var_type: data_type, name: name.value, debug_data: parser.debug_data(), }) }}fn handle_function_declaration( output_data_type: DataType, name: String, parser: &mut Parser,) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::OpenParen)?;
let mut properties = Vec::new();
if parser.current().kind != TokenKind::CloseParen { loop { let data_type = types::parse(parser).context("parse function input data types")?; let name = parser.expect(TokenKind::Identifier)?.value.to_owned(); properties.push(Property { var_name: name, var_type: data_type, }); if parser.current().kind == TokenKind::CloseParen { break; } parser .expect(TokenKind::Comma) .context("function properties")?; } } parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseParen)?; parser.expect(TokenKind::OpenCurly)?;
let mut inside = Vec::new(); while parser.current().kind != TokenKind::CloseCurly { inside.push(parsing_functions::expression(parser, 0).context("inside function")?); if parser.current().kind == TokenKind::SemiColon { parser.advance(); } }
parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseCurly)?; Ok(Expression::Function { name, properties, output: output_data_type, inside: inside, debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}use crate::{ lexer::token::TokenKind, parser::{self, Parser, expression::Expression, types},};pub mod data_parsing;pub mod identifier_parsing;pub mod statement_parsing;use anyhow::{Context, Result};use log::info;
pub fn function_call(parser: &mut Parser, left: Expression, _: i8) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::OpenParen)?; let mut properties = Vec::new(); loop { let current_token = parser.current().to_owned(); properties.push( expression(parser, 0).with_context(|| { format!("function call- parse input values-> {:?}", current_token) })?, );
if parser.current().kind == TokenKind::CloseParen { break; } parser.advance(); } parser .expect(TokenKind::CloseParen) .context("function_cal -> end paren")?;
Ok(Expression::FunctionCall { left: Box::new(left), values: properties, debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}
pub fn assignment(parser: &mut Parser, left: Expression, _: i8) -> Result<Expression> { let operator = parser.advance().to_owned(); let value = Box::new(expression(parser, 0)?); Ok(Expression::Assignment { target: Box::new(left), operator, value, debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}
pub fn return_expr(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::Return)?; let value = expression(parser, 0)?; Ok(Expression::Return { value: Box::new(value), debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}pub fn expression(parser: &mut Parser, bp: i8) -> Result<Expression> { let mut current_expression = { let nod_function = parser.current_stats()?.nod_function.with_context(|| { format!( "expected token kind: '{:?}' to have nod function.", parser.current().kind ) })?; let current_token = parser.current().to_owned(); nod_function(parser) .with_context(|| format!("parse expression, nod- {:?}", current_token))? };
while let current_stats = parser.current_stats()? && current_stats.binding_power > bp { let led_function = current_stats.led_function.with_context(|| { format!( "expected token kind: '{:?}' to have a led function.", parser.current().kind ) })?;
let current_token_for_dbg = parser.current().to_owned(); let current_expr_for_dbg = current_expression.to_owned();
current_expression = led_function(parser, current_expression, current_stats.binding_power) .context(format!( "parse expression, led- {:?}, current expression: {:?}", current_token_for_dbg, current_expr_for_dbg ))?; }
return Ok(current_expression);}
pub fn binary(parser: &mut Parser, left: Expression, bp: i8) -> Result<Expression> { let operator = parser.advance().to_owned(); let right = expression(parser, bp).context("binary operation- parse expression on the right")?;
Ok(Expression::Binary { left: Box::new(left), operator: operator, right: Box::new(right), debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}
pub fn compiler_data(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { Ok(Expression::CompilerData( parser.advance().value.to_owned(), parser.debug_data(), ))}
pub fn prefix(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { let prefix = parser.advance().to_owned(); let value = expression(parser, 0).context("prefix")?;
return Ok(Expression::Prefix { prefix, value: Box::new(value), debug_data: parser.debug_data(), });}pub fn break_expr(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::Break)?; return Ok(Expression::Break { debug_data: parser.debug_data(), });}pub fn open_paren(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::OpenParen)?;
let current = parser.current(); if current.kind == TokenKind::Identifier && parser .valid_data_type_names .contains(current.value.as_str()) { let data_type = types::parse(parser).context("open_paren -> TypeConversion -> data_type")?; parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseParen)?; let value = expression(parser, 0).context("open_paren -> TypeConversion -> value")?;
Ok(Expression::TypeConversion { value: Box::new(value), data_type, debug_data: parser.debug_data(), }) } else { let value = Box::new(expression(parser, 0)?);
parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseParen)?; Ok(Expression::Grouping { value, debug_data: parser.debug_data(), }) }}pub fn member_expr(parser: &mut Parser, left: Expression, _: i8) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::Dot)?; let right = expression(parser, 0).with_context(|| format!("member expr-> left:{:?}", left))?;
Ok(Expression::MemberExpr { left: Box::new(left), right: Box::new(right), debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}pub fn array_access(parser: &mut Parser, left: Expression, _: i8) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::OpenBracket)?; let index = expression(parser, 0)?;
parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseBracket)?; Ok(Expression::ArrayAccess { left: Box::new(left), index: Box::new(index), debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}
pub fn static_expr(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::Static)?; let value = expression(parser, 0)?; Ok(Expression::Static { value: Box::new(value), debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}pub fn type_def(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::Typedef)?; let data_type = types::parse(parser).context("type_def -> data_type")?; let name = parser .expect(TokenKind::Identifier) .context("type_def -> name")? .value;
parser.valid_data_type_names.insert(name.to_string());
Ok(Expression::Typedef { data_type, name, debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}
pub fn dereference(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::Star)?; let value = expression(parser, 0)?;
Ok(Expression::Dereference { value: Box::new(value), debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}
pub fn decrement(parser: &mut Parser, left: Expression, _: i8) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::MinusMinus)?; Ok(Expression::Decrement { target: Box::new(left), debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}pub fn increment(parser: &mut Parser, left: Expression, _: i8) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::PlusPlus)?; Ok(Expression::Increment { target: Box::new(left), debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}
pub fn access_reference(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::Reference)?; let value = expression(parser, 0)?;
Ok(Expression::AccessReference { value: Box::new(value), debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}use std::collections::vec_deque;
use anyhow::{Context, Result};use log::info;
use crate::{ lexer::token::TokenKind, parser::{ Parser, expression::Expression, parsing_functions::{self, expression}, },};pub fn parse_open_curly(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::OpenCurly)?; // this might not be the best way to do this, but i don't see another one for now if parser.next().kind == TokenKind::Comma { parse_data_structure_initialization(parser) } else { new_code_block(parser) }}
pub fn new_code_block(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { let mut inside = Vec::new(); while parser.current().kind != TokenKind::CloseCurly { inside.push(parsing_functions::expression(parser, 0).with_context(|| { format!( "debug data: {:?},\n parsed expressions:{:#?}", parser.debug_data(), inside ) })?); if parser.current().kind == TokenKind::SemiColon { parser.advance(); } } parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseCurly)?;
Ok(Expression::NewCodeBlock { inside, debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}pub fn parse_data_structure_initialization(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { let mut values = Vec::new(); loop { let value = expression(parser, 0)?; values.push(value); if parser.current().kind == TokenKind::CloseCurly { break; } parser.expect(TokenKind::Comma)?; } parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseCurly)?;
Ok(Expression::DataStructureInitialization { values, debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}
pub fn parse_if(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::If)?; parser.expect(TokenKind::OpenParen)?; let condition = parsing_functions::expression(parser, 0)?; parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseParen)?; parser.expect(TokenKind::OpenCurly)?; let mut inside = Vec::new(); while parser.current().kind != TokenKind::CloseCurly { inside.push(parsing_functions::expression(parser, 0)?); parser .expect(TokenKind::SemiColon) .context("expected to find a semicolon after a expression - function contents")?; } parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseCurly)?;
let mut chained_elses = Vec::new();
while parser.current().kind == TokenKind::Else { let (else_value, break_else) = parse_else(parser)?; chained_elses.push(else_value); if break_else { break; } }
Ok(Expression::If { condition: Box::new(condition), inside, chained_elses, debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}fn parse_else(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<(Expression, bool)> { parser.expect(TokenKind::Else)?; let (break_else, condition) = if parser.current().kind == TokenKind::If { parser.expect(TokenKind::If)?; parser.expect(TokenKind::OpenParen)?; let condition = parsing_functions::expression(parser, 0)?; parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseParen)?; (false, Some(Box::new(condition))) } else { (true, None) }; parser.expect(TokenKind::OpenCurly)?;
let mut inside = Vec::new(); while parser.current().kind != TokenKind::CloseCurly { inside.push(parsing_functions::expression(parser, 0)?); parser .expect(TokenKind::SemiColon) .context("expected to find a semicolon after a expression - function contents")?; } parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseCurly)?; Ok(( Expression::Else { condition, inside, debug_data: parser.debug_data(), }, break_else, ))}
pub fn parse_while(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { parser.expect(TokenKind::While)?; parser.expect(TokenKind::OpenParen)?; let condition = parsing_functions::expression(parser, 0)?; parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseParen)?; parser.expect(TokenKind::OpenCurly)?; let mut inside = Vec::new(); while parser.current().kind != TokenKind::CloseCurly { inside.push(parsing_functions::expression(parser, 0)?); parser .expect(TokenKind::SemiColon) .context("expected to find a semicolon after a expression - function contents")?; } parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseCurly)?;
Ok(Expression::While { condition: Box::new(condition), inside, debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}
pub fn parse_for(parser: &mut Parser) -> Result<Expression> { // for(int i =0;i<25;i++){ // ... // } parser.expect(TokenKind::For)?; parser.expect(TokenKind::OpenParen)?; let iterator_init = Box::new(parsing_functions::expression(parser, 0)?); parser.expect(TokenKind::SemiColon)?; let condition = Box::new(parsing_functions::expression(parser, 0)?); parser.expect(TokenKind::SemiColon)?; let incr = Box::new(parsing_functions::expression(parser, 0)?); parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseParen)?;
parser.expect(TokenKind::OpenCurly)?; let mut inside = Vec::new(); while parser.current().kind != TokenKind::CloseCurly { inside.push(parsing_functions::expression(parser, 0)?); parser .expect(TokenKind::SemiColon) .context("expected to find a semicolon after a expression - function contents")?; } parser.expect(TokenKind::CloseCurly)?;
Ok(Expression::For { iterator_init, condition, incr, inside, debug_data: parser.debug_data(), })}and our token stats should look like this:
use std::collections::HashMap;
use crate::{ lexer::token::TokenKind, parser::{ Parser, expression::Expression, parsing_functions::{self, open_paren, identifier_parsing}, },};use anyhow::Result;
type NodFunction = fn(&mut Parser) -> Result<Expression>;type LedFunction = fn(&mut Parser, left: Expression, bp: i8) -> Result<Expression>;pub struct TokenStats { pub binding_power: i8, pub nod_function: Option<NodFunction>, pub led_function: Option<LedFunction>,}pub fn token_stats() -> HashMap<TokenKind, TokenStats> { HashMap::from([ ( TokenKind::EndOfFile, TokenStats { binding_power: -1, nod_function: None, led_function: None, }, ), ( TokenKind::SemiColon, TokenStats { binding_power: -1, nod_function: None, led_function: None, }, ), ( TokenKind::BitwiseShiftLeft, TokenStats { binding_power: 2, nod_function: None, led_function: Some(parsing_functions::binary), }, ), ( TokenKind::BitwiseShiftRight, TokenStats { binding_power: 2, nod_function: None, led_function: Some(parsing_functions::binary), }, ), ( TokenKind::Plus, TokenStats { binding_power: 2, nod_function: Some(parsing_functions::prefix), led_function: Some(parsing_functions::binary), }, ), ( TokenKind::Minus, TokenStats { binding_power: 2, nod_function: Some(parsing_functions::prefix), led_function: Some(parsing_functions::binary), }, ), ( TokenKind::Star, TokenStats { binding_power: 3, nod_function: Some(parsing_functions::dereference), led_function: Some(parsing_functions::binary), }, ), ( TokenKind::Slash, TokenStats { binding_power: 3, nod_function: None, led_function: Some(parsing_functions::binary), }, ), ( TokenKind::Percent, TokenStats { binding_power: 3, nod_function: None, led_function: Some(parsing_functions::binary), }, ), ( TokenKind::Equals, TokenStats { binding_power: 4, nod_function: None, led_function: Some(parsing_functions::binary), }, ), ( TokenKind::NotEquals, TokenStats { binding_power: 4, nod_function: None, led_function: Some(parsing_functions::binary), }, ), ( TokenKind::Less, TokenStats { binding_power: 4, nod_function: None, led_function: Some(parsing_functions::binary), }, ), ( TokenKind::LessEquals, TokenStats { binding_power: 4, nod_function: None, led_function: Some(parsing_functions::binary), }, ), ( TokenKind::Greater, TokenStats { binding_power: 4, nod_function: None, led_function: Some(parsing_functions::binary), }, ), ( TokenKind::GreaterEquals, TokenStats { binding_power: 4, nod_function: None, led_function: Some(parsing_functions::binary), }, ), ( TokenKind::Or, TokenStats { binding_power: 1, nod_function: None, led_function: Some(parsing_functions::binary), }, ), ( TokenKind::And, TokenStats { binding_power: 1, nod_function: None, led_function: Some(parsing_functions::binary), }, ), ( TokenKind::Not, TokenStats { binding_power: 1, nod_function: Some(parsing_functions::prefix), led_function: Some(parsing_functions::binary), }, ), ( TokenKind::Number, TokenStats { binding_power: 0, nod_function: Some(parsing_functions::data_parsing::number), led_function: None, }, ), ( TokenKind::String, TokenStats { binding_power: 0, nod_function: Some(parsing_functions::data_parsing::string), led_function: None, }, ), ( TokenKind::Identifier, TokenStats { binding_power: 0, nod_function: Some(identifier_parsing::identifier), led_function: None, }, ), ( TokenKind::Return, TokenStats { binding_power: 0, nod_function: Some(parsing_functions::return_expr), led_function: None, }, ), ( TokenKind::CloseParen, TokenStats { binding_power: 0, nod_function: None, led_function: None, }, ), ( TokenKind::OpenParen, TokenStats { binding_power: 5, nod_function: Some(parsing_functions::open_paren), led_function: Some(parsing_functions::function_call), }, ), ( TokenKind::True, TokenStats { binding_power: 0, nod_function: Some(parsing_functions::data_parsing::boolean), led_function: None, }, ), ( TokenKind::False, TokenStats { binding_power: 0, nod_function: Some(parsing_functions::data_parsing::boolean), led_function: None, }, ), ( TokenKind::CloseCurly, TokenStats { binding_power: 0, nod_function: None, led_function: None, }, ), ( TokenKind::CompilerData, TokenStats { binding_power: 0, nod_function: Some(parsing_functions::compiler_data), led_function: None, }, ), ( TokenKind::Typedef, TokenStats { binding_power: 0, nod_function: Some(parsing_functions::type_def), led_function: None, }, ), ( TokenKind::PlusEquals, TokenStats { binding_power: 5, nod_function: None, led_function: Some(parsing_functions::assignment), }, ), ( TokenKind::MinusEquals, TokenStats { binding_power: 5, nod_function: None, led_function: Some(parsing_functions::assignment), }, ), ( TokenKind::StarEquals, TokenStats { binding_power: 5, nod_function: None, led_function: Some(parsing_functions::assignment), }, ), ( TokenKind::SlashEquals, TokenStats { binding_power: 5, nod_function: None, led_function: Some(parsing_functions::assignment), }, ), ( TokenKind::PlusPlus, TokenStats { binding_power: 5, nod_function: None, led_function: Some(parsing_functions::increment), }, ), ( TokenKind::MinusMinus, TokenStats { binding_power: 5, nod_function: None, led_function: Some(parsing_functions::decrement), }, ), ( TokenKind::Equals, TokenStats { binding_power: 5, nod_function: None, led_function: Some(parsing_functions::assignment), }, ), ( TokenKind::Reference, TokenStats { binding_power: 5, nod_function: Some(parsing_functions::access_reference), led_function: None, }, ), ( TokenKind::Static, TokenStats { binding_power: 0, nod_function: Some(parsing_functions::static_expr), led_function: None, }, ), ( TokenKind::OpenBracket, TokenStats { binding_power: 5, nod_function: None, led_function: Some(parsing_functions::array_access), }, ), ( TokenKind::CloseBracket, TokenStats { binding_power: 0, nod_function: None, led_function: None, }, ), ( TokenKind::OpenCurly, TokenStats { binding_power: 0, nod_function: Some(parsing_functions::statement_parsing::parse_open_curly), led_function: None, }, ), ( TokenKind::Comma, TokenStats { binding_power: 0, nod_function: None, led_function: None, }, ), ( TokenKind::While, TokenStats { binding_power: 0, nod_function: Some(parsing_functions::statement_parsing::parse_while), led_function: None, }, ), ( TokenKind::For, TokenStats { binding_power: 0, nod_function: Some(parsing_functions::statement_parsing::parse_for), led_function: None, }, ), ( TokenKind::If, TokenStats { binding_power: 0, nod_function: Some(parsing_functions::statement_parsing::parse_if), led_function: None, }, ), ( TokenKind::Dot, TokenStats { binding_power: 1, nod_function: None, led_function: Some(parsing_functions::member_expr), }, ), ( TokenKind::Unsigned, TokenStats { binding_power: 0, nod_function: Some( parsing_functions::identifier_parsing::handle_function_or_variable_declaration, ), led_function: None, }, ), ])}